Zero trust is not a new concept. However, the pandemic and the transformation toward a more digital society are highlighting issues that haven't previously been on the radar making zero trust security a hot topic.
Today there are more connected Internet of Things (IoT) devices in use than ever. These technologies are designed to provide a single service, and unfortunately, security is not the device's priority. The lack of in-built security makes IoT devices vulnerable to attacks, as well, it creates a potential route into an organization's entire network.
As companies embark on their digital transformation journey it is imperative that their network infrastructure is secure. Network segmentation, a principle of zero trust security, makes it possible to prevent attacks. As soon as a compromise is reported, the potential for an attack can be reduced and lateral movements on the network can be limited, so as not to affect other connected systems.
Zero Trust-at-a-Glance
In business computing and enterprise environments, network segmentation has two approaches depending on the existing degree of trust. Traditionally, the boundary of trust has been physical and implicit, so the computer network was protected by a firewall. What that means in the simplest of terms is - what's inside is protected from the outside. However, this approach has had to evolve as threat risks have increased.
In the zero trust world, trust is dynamic and adaptable and no longer assumed, even within the network. The guiding principle is ‘never trust – always verify’, that means acting as if there are already attackers present in the system. With this principle in mind, the first step is Network Access Control (NAC), the identification of objects, and authentication of connected users. Based on these factors, macro-segmentation is set up using firewalls to filter traffic between different classes of objects and users. For example, you can isolate surveillance cameras and building management sensors. Then, based on identification, a second level of filtering within a segment makes it possible to refine and achieve micro-segmentation. In this second step, the goal is to prevent the surveillance cameras from communicating with each other within the same network segment.
Why Zero Trust is so Important Now
Over the past 18 months cyberattacks have been on the rise, and the costs to businesses have been significant. In addition, hackers are executing increasingly sophisticated and malicious attacks. Because zero trust requires the identification and authentication of each device and user before allowing access to the network, it is possible to contain, and even avoid attacks. This is due to network segmentation which restricts the range of access and reduces the spread of attack.
With an intelligent mix of macro- and micro-segmentation the zero trust approach provides a restricted and mobile security perimeter around each user and object. Organizations manage network access controls, define authorizations (for example access by job role), and are able to secure and contain threats, as the network continually searches for inappropriate or suspicious behavior.
New network functionalities enable zero trust, which is proportionately increasing the level of defense against expanded and sophisticated cyberattacks.
Five Steps to Your Zero Trust Network
While it is pretty easy to build a zero trust secure network from scratch (for example, new premises, new structure), however, most companies already have an existing network in place. The challenge for these organizations is to harmonize approaches to meet the needs of the organization, while securing it from attacks. Following are five steps to zero trust:
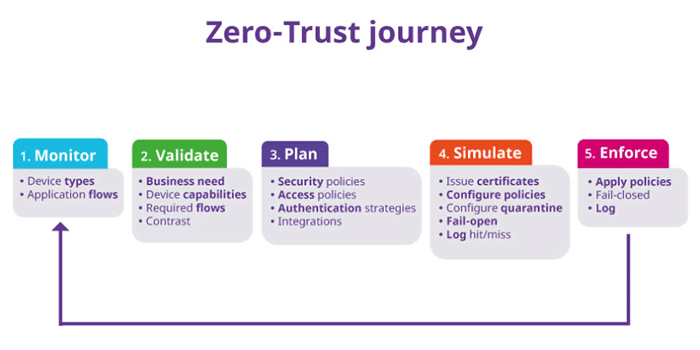
- Monitor: Identify all equipment, peripherals, connected devices and authenticate all the people that have access to the network. An object inventory is created and populated automatically.
- Validate: Control all the connected devices and invalidate those not justified for the activity, as they increase the possibility of attack. Apply the principle of least privilege which grants the minimum permissions required to perform a task. If the network identifies non-compliant equipment, it will be necessary to implement a restoration or remediation plan.
- Plan: Know all the users' equipment, as well as their workflow and the traffic generated to transform this data into a security policy that intelligently combines macro-segmentation (input/output control) and micro-segmentation (fine-grained security rules)
- Simulate: Apply in parallel identification, authentication, and security policy in "fail open" mode: All equipment will be authorized and network behavior logged and indexed, in order to set up authorization schemes and an adapted network security policy. This critical step will refine the security policy while ensuring that normal activity is not impacted.
- Enforce: In the final step the "fail open" becomes "fail close:" Authentication failures are no longer tolerated, all unreferenced users or devices are refused, all illegitimate flows are stopped. Network monitoring is immediate to verity that all devices are identified, users are authenticated to be authorized on the network or possibly quarantined while security checks take place.
In a Nutshell
The zero trust approach makes it possible to identify traffic, automatically store objects in an inventory, create scheduled rules for the network, and share user and IoT profiles according to rules. It also makes it possible to determine the central IDS or switches' DoS attacks, and optionally apply quarantine for suspicious flows in a restricted and dynamic perimeter.
Zero trust provides an authentication strategy and a consistent security policy across your network infrastructure, implemented in-line with the needs of users and connected technologies. The intelligent combination of macro-segmentation and micro-segmentation, with quarantine in the event of a breach of security rules, ensures the highest degree of security for your network infrastructure. In an increasingly volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous world, the zero trust approach is your best bet to ensure your network and business assets security.
Learn more about how SMC can help boost your network security.
Article Source:
Alcatel Lucent